Day 2 :
Keynote Forum
Azlina Abd. Aziz
Universiti Malaysia Terengganu,Malaysia
Keynote: Energy Resources in the Coastal Countries of the South China Sea: An Empirical Analysis of Energy Demand and Its Determinants
Time : 09:00-09:40

Biography:
Azlina Abd. Aziz is a Senior Lecturer at the School of Social Development and Economics of Universiti Malaysia Terengganu. She received her B.Econ (Hons) in Analytical Economics and Master’s degree in Economics from University of Malaya in 1999 and 2002 respectively. She obtained her Ph.D. degree in Economics from University of Leicester in 2007. Her fields of interest are environmental and natural resource economics, particularly Energy Economics. Among her current areas of research are energy demand and economic growth, energy and the environment, energy consumer behavior and low carbon/renewable energy economics. She has presented papers at conferences both home and abroad, published articles and papers in various journals.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Developing countries play an increasingly important role in the world energy markets, with their consumption of energy increasing significantly over the past two decades. According to a report released by the United States Energy Information Administration (EIA, 2013) these countries will account for 65 per cent of the world’s energy consumption by the year 2040. The increase has been particularly pronounced among the developing countries of East and Southeast Asia and is expected to continue into the next century. The increasing importance of the share of developing economies in the global energy markets also means there will be excessive increase in energy consumption which posed obstacles to economic development. The present paper aims to identify the key economic forces driving changes that influence energy demand.
Recent Publications:
- A.A. Azlina, Mahirah Kamaludin, Engku Siti Zaharah Engku Abdullah, Alias Radam (2016), Factors Influencing Household End-Use Electricity Demand in Malaysia, Advanced Science Letter, Vol. 22 Number 12, pp.4120-4123.
- 2. K. Mahirah, A.A. Azlina, Izyan Nazirah & Ridzuan Yacob (2015), Valuing Road User’s Willingness to Pay to Reduce Traffic Congestion in Klang Valley, Malaysia, Asian Social Science, Vol. 11, No. 25:x-xISSN 1911-2017 E-ISSN 1911-2025.
- A.A. Azlina, Engku Siti Zaharah Engku Abdullah, Mahirah Kamaludin & Alias Radam (2015), Energy Conservation of Residential Sector In Malaysia, Journal of Business & Social Development, Vol. 3 Number 2: 51-62. ISSN: 2289-2915.
- A.A. Azlina, Siong Hook Law & Nik Hashim Nik Mustapha (2014), Dynamic linkages among transport energy consumption, income and CO2 emission in Malaysia, Energy Policy, Vol. 73: 598-606. ISSN: 0301-4215.
- A.A Azlina, Nik Hashim Nik Mustapha, Roslina Ismail (2013), Factors Affecting Energy Demand in Developing Countries: A Dynamic Panel Analysis, International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, Vol. 3: 1-6. ISSN Online: 2146-4553 Factor: 0.608).
Keynote Forum
Taha Elhag
Heriot Watt University, UAE
Keynote: Pipelines maintenance Management System
Time : 10:40-11:05

Biography:
Taha Elhag is an Associate Professor in Project Management at Heriot Watt University. Previously he was an Associate Professor at UCL, University of London and was an Assistant Professor at Manchester University, UK. His teaching duties comprise undergraduate and postgraduate programs; and Course Directorship. His academic experience also includes the supervision of MSc dissertations and PhD research and acting as Internal and External Examiner for different universities. He is also an expert Reviewer for many international journals and EPSRC research projects. He was a Visiting Lecturer at Manchester and Reading Universities and the British University in Dubai (BUiD). He is an internationally respected academic with a track record of publications. He is the author of over 60 refereed papers in international journals and conferences.
Abstract:
During recent years, many systems and models have been developed for inspecting, monitoring and managing the maintenance of oil/gas pipelines. However, the adoption and application of these systems by the industry have not been very effective. On the other hand, the reliability of some condition assessment systems is not very efficient because of: (1) the subjective nature of monitoring data interpretation by experts; and (2) the complex relationships between the many types of defects. Dawotola et al. (2013) developed an integrity maintenance optimization framework for petroleum pipelines for the determination of the probability of failures and their associated consequences. Hovhanessian et al. (2008) developed pipeline risk management system for lifetime prediction and to establish priorities for monitoring activities. Otegui (2014) investigated the conditions contributed to failures of buried pipelines. The study concluded that the most frequent threats for the integrity of onshore buried pipelines are corrosion and third party damage, as well as loss of data about material and operation, old repairs and demographic changes. Due to the constraints of time, budget and other resources such as manpower and equipment, it is not possible for oil and gas assets owner organizations to either attend to all maintenance requirement schemes within a given planning period or to perform all the planned maintenance concurrently. Accordingly, the primary objectives of this research is to investigate and rank the significant parameters governing the decision making process for priority rating of repair and maintenance activities for oil/gas pipelines and to develop an integrated pipeline maintenance management system.
- Global Business | Hydrocarbon Exploration | Petrochemistry | Petroleum Science and Technology | Upstream Process
Location: Berlin, Germany

Chair
Abdel Moktader a. El Sayed
Ain Shams University, Egypt

Co-Chair
Mehmet Efe Biresselioglu
Izmir University of Economics, Turkey
Session Introduction
Abdel Moktader A El Sayed
Ain Shams University, Egypt
Title: Petrophysical study of Szolnok Formation, Endrod gas field, Hungary
Time : 10:40-11:05

Biography:
Abdel Moktader A El Sayed has expertise in reservoir geophysics and petrophysics. He is an Emeritus Professor in Department of Geophysics of Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt. He has studied different types of hydrocarbon reservoirs for more than 45 years. He has used different laboratory instruments for outlining MICP, SEM, NMR and others. He has published more than 78 scientific articles in international and national periodicals. He is a Member of several scientific societies in Egypt and abroad specialized in geology and geophysics.
Abstract:
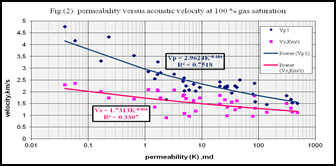
Investigation of rock porosity and permeability is highly beneficial for geologists, petro-physicist and petroleum engineers in order to evaluate reservoir anisotropy and its pore space geometry through the time and space. Clastic reservoir quality and classification could perform based on these data correlations. The Szolnok Formation in the great Hungarian plain is composed mainly of sandstones intercalated with marl and siltstones of delta fringe deposits. In the present study, 213 core samples were obtained from the Szolnok Formation and subjected for petrophysical investigations. Both horizontal and vertical permeability were measured with different techniques. Permeability anisotropy gives unambiguous diagnostic features for reservoir heterogeneity in case of siltstone marl facies. The study of grain size parameters and cross-plots constructed among measured reservoir properties indicate that Szolnok Formation has two main lithologic facies: Clean sandstone (represented in this study by 141 samples) and siltstone marl (represented by 72 samples). From the interpretation of measured data, it can obviously differentiate among good, intermediate and bad reservoir rocks in Szolnok Formation. Ultrasonic laboratory measurements were carried out for only 30 sandstone core samples. These samples were completely dry, while Sonic Viewer-120 instrument is used to measure seismic velocity, Poisson’s ratio and other mechanical properties such as rigidity, bulk modulus and Young’s modulus. Both Wyllie and Raymer equations were used to predict reservoir porosity in order to relate it to measured porosity. Effective pore radius is outlined from both porosity and permeability.
Recent Publications
- El Sayed, A.M.A.(2011)Thermophysical properties of sandstone reservoir rocks. J. of Petroleum Science and Engineering 76:138-147.
- El Sayed, A. M. A. and Abbass, A. (2009) PVC-migration controles reservoir parameters: Szolnok Formation, Endrod field, Hungary.11th international Conference of Mining, Petroleum and Metallurgical Engneering.789-801.
- El Sayed, A. M. A. and El Sayed, N.A.(2016)Petrophysical properties of clastic reservoirs. Journal of Geophysics and Geochemistry. 3(3):28-32.
- El Sayed, A.M.A., Abu seda, H. and El Sayed, N.A. (2017) Petrophysical study of Szolnok Formation, Endrod Gas field, Hungary. EJPE, 26:198-202.
- Sari, K. (2013) Comparing log analysis and well logs using a Hungarian gas field as example. NAFTA 64(2):107-117.
Behzad Rostami
University of Tehran, Iran
Title: Impact of pure CO2 and carbonated water injection to enhance recovery of Heavy oil

Biography:
Behzad Rostami (Corresponding Author) is an associate Professor of petroleum engineering in the Institute of Petroleum Engineering (IPE) at University of Tehran. His research interests involve gas injection based methods of enhanced oil recovery, foam injection and carbonated water injection, CO2 sequestration in Saline aquifers and depleted hydrocarbon reservoirs, gravity drainage and multi block interaction in fractured media. Rostami has authored more than 40 technical papers in international journals and also supervised more than 30 graduate students.
Abstract:
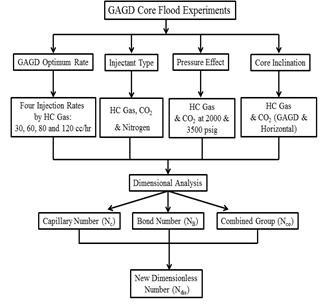
Performance of CO2 and hydrocarbon (HC) gas injection into a heavy crude oil was investigated at high pressure/temperature condition, using high permeable well-sorted original reservoir sandstone. Complete series of PVT and slime tube tests were followed by vertical and horizontal gas floods to study the impact of injection rate, injectant type and reservoir pressure. Dimensional analysis was performed to study the involved mechanism and forces. Sometimes direct injection of CO2 may not be practically and economically possible. In addition, in plans for CO2 storage, CO2 as a free phase in a reservoir is coupled with a significant leakage risk that prevents the scenario of direct injection. Therefore, in the second part, the enhancement of heavy oil recovery was tested by the carbonated water injection. The results of the first part of core flooding experiments demonstrated that gravity and solubility are the most effective mechanisms in oil recovery. The reduction in oil recovery in horizontal flooding for HC gas injection is higher due to the smaller difference between the densities of CO2 and oil compared to HC gas/oil systems. Furthermore, a small increase of oil recovery after breakthrough (BT) during N2 injection proves the importance of the solubility mechanism. Therefore, In this case, more precised analysis could be performed by applying the dissolution number instead of Capillary and/or Bond number.
Recent Publications:
- Mirazimi, S., Rostami,B., Ghazanfari, M.H., Khosravi, M., (2017) " Water film rupture in blocked oil recovery by gas injection Experimental and modeling study", Chemical Engineering Science”.161. 288–298.
- Zeinabadi, D., Rostami B., Khosravi, M., (2016) “Effect of petro physical matrix properties on Bypassed oil Recovery from a matrix-fracture system during CO2 near-miscible injection: experimental investigation”, International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 85, 123-131.
- Kazemi, K., Rostami, B., Khosravi, M., Zeinabadi, D., (2015) “Effect of initial Water Saturation on Bypassed Oil Recovery during CO2 injection at different Miscibility Condition”, Energy & Fuels. 29(7).
- Khostavi. M., Rostami, B., Emadi, M., Roayaie, E. (2015), “Marangoni Flow: An Unknown Mechanism of oil Recovery during Near-Miscible CO2 injection”, Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 125, 263-268.
- Fatollahi, A., Rostami, B. (2014), “Carbonated Water Injection: Effects of Silica Nano-Particles and Operating Pressure”, The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 93(11).
Mehmet Efe Biresselioglu
Izmir University of Economics, Turkey
Title: Structuring a sustainable, fully competitive and liberal natural gas market in Turkey: The perception of the Turkish private sector

Biography:
Mehmet Efe Biresselioglu is an Associate Professor of Energy Security and Policy in the Department of Political Science and International Relations and Head of Sustainable Energy Division at Izmir University of Economics, Turkey. He is also acting as the Steering Committee Member of European Energy Research Alliance’s (EERA) “e3s” Joint Program and the Head of Izmir Circle of Mediterranean Citizens’ Assembly (ACIMEDIT). He has completed his PhD at IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, Italy. He has received his MA in European Studies from Jean Monnet Center of Excellence at University of Turku, Finland and his BA in Political Science and Public Administration from Bilkent University, Turkey. His research interest is in the area of energy security, energy policy analysis and energy economics. He has published several articles in the leading journals such as Energy Policy, Renewable Energy, Energy and Energy Research & Social Science.
Abstract:
In Turkey, natural gas was first introduced in 1986. Following that, the use of natural gas has become rapidly widespread and started to be used for electricity generation, residential heating and industry, together with the increasing energy needs resulting from the rapid economic and population growth. Especially in the last 15 years, Turkey has become one of the leading countries with fastest-growing natural gas demand. Over the last 30 years, Turkey’s annual natural gas consumption growth rate is 18%, tripling its total energy consumption growth rate in the same period. However, it comes with a burden. The decision of increasing the use of natural gas in Turkey makes it highly import dependent, 99%, decreasing the level of security of supply. Hence, Turkish natural gas consumption has already reached to 4635 bcm as of the end of 2016 in Turkey, doubling the 2003 levels, representing 30% of Turkey’s primary energy consumption. However, Turkey was not successful in establishing a liberal natural gas market. Turkish Petroleum Pipeline Corporation (BOTAS) is responsible for almost 80% of the natural gas imports, much higher compared to private sector’s share.
Recent Publications:
- M.E. Biresselioglu, C. Yildirim, M.H. Demir, S. Tokcaer (2017), “Establishing an energy security framework for a fast-growing economy: Industry perspectives from Turkey”, Energy Research & Social Science, Volume 27, May 2017, Pages 151-162 (ESCI)
- M.E. Biresselioglu, T. Yelkenci, E. Ozyorulmaz, I.O. Yumurtaci (2017) "Interpreting Turkish industry's perception on energy security: A national survey", Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, January, Vol. 67, pp.1208-1224 (SCI)
- M.E. Biresselioglu, D. Kilinc, E. Onater-Isberk, T. Yelkenci, “Estimating the political, economic and environmental factors’ impact on the installed wind capacity development: A system GMM approach”, Renewable Energy, Vol.96, Part A, October, p. 636-644 (2016) (SCI-Expanded)
- M.E. Biresselioglu, T. Yelkenci, “Scrutinizing the Causality Relationships between Prices, Production and Consumption of Fossil Fuels: A Panel Data Approach”, Energy, Vol. 102, p.44-53 (2016) (SCI)
- M.E. Biresselioglu “Changing Trends in the Production and Consumption of Oil and Natural Gas in the World” in M.R. Riazi (ed), Exploration and Production of Petroleum and Natural Gas, ASTM International, p. 657-678 (2016)
Dewei Meng
Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, China
Title: Research on well type and well pattern optimization for tight gas recovery enhancement

Biography:
Dewei Meng began his professional career at Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development (RIPED) in 2008, having abundant experience in unconventional gas development for nearly 10 years. He is mainly engaged in development and evaluation of low permeability & tight gas reservoir and has made great contributions to improving reservoir engineering. He has published more than 10 papers in reputed journals.
Abstract:
Tight gas, the first large-scale used unconventional natural gas has been extremely important in Chinese energy domain. According to statistics in 2015, proven geological reserve of tight gas accounts for more than 30% in that of nature gas. Meanwhile its production accounts for 25% of nature gas output. Under such circumstances, tight gas development mainly faces three kinds of challenges: Firstly, newly built gas fields are needed for supplementation during field production decreasing; secondly, gas production ratio is largely affected by constant fluctuations of gas price and gradually decreased quality of newly developed reserves; thirdly, tight gas recovery needs to be enhanced dramatically since the general recovery factor is quite low, just around 35%. Therefore, how to guarantee stable development and enhance recovery factor of tight gas in a long run are the main problems during tight gas reservoir development. In this study, Sulige gas field, the largest natural gas field in China, is taken for an example, mainly from well pattern optimization. Six specific aspects are taken in to account and they are fine reservoir characterization, 3D geological modeling of complex reservoir and distribution characteristics of remaining gas, well pattern infilling in developing area, recovery factor enhancement by horizontal wells and mixed well pattern. The results and methods are used for long-term and stable development in tight gas field.
Guo Jianlin
Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, China
Title: Reservoir characterization of typical tight gas in China

Biography:
Guo Jianlin has received his BS degree in Petroleum Geology from the China University of Geoscience and his MS and PhD degrees from Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development (RIPED), Beijing, China. From 1998, he has worked in the areas of oil & gas geology, reservoir modeling and engineering. He is currently a Senior Engineer of Department of Ordos E&P, RIPED, working mainly on gas development.
Abstract:
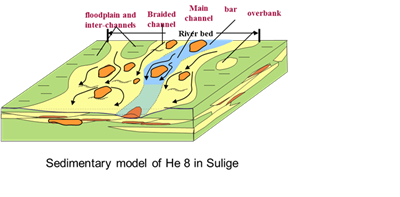
After more than ten years of tight gas development practice and technical research, China has successfully solved the technical problems of tight gas development, and it has become the most important contributor to China's natural gas production. Due to the strong heterogeneity of the tight gas reservoir, reserves producing degree and recovery rate is low, it needs more fine geological guidance to solve these problems, so the reservoir characterization of tight gas is crucial. This paper takes the Sulige gas field (the largest gas field in china) as a case study, because of its low abundance and strong heterogeneity, it is challenging for large scale commercial development of this field. Therefore, it is necessary to study the basic characteristics of effective reservoir and first of all, looking for sweet spots is currently the priority. Comprehensive geological study confirmed that the reservoirs with coarse grain, high content of quartz are more easily lead to dissolution which is the most constructive diagenesis in Sulige gas field and the dissolved pores are almost the basis of high quality reservoirs. So the sweet spots are located in the coarse grained sand bodies with high content quartz and these sand bodies are mainly distributed in the lower part of the channel deposits and channel bar deposits. Now the answer is obvious, predicting channels especially the main river channels distribution is the key to search for sweet spots. Through seismic and geological study, first set up the typical log and seismic response characteristics of different types of sands, then carry out sedimentary facies, diagenesis, reservoir evaluation study and so on, finally simulate the channel development. On the base of the geological models, we can predict the sweet spots distribution. This technology has been applied in many blocks of Sulige gas field, the proportion of higher effective wells drilled in the past 5 years increased by a big margin.
Recent Publications:
- Jia Ailin, Guo Jianlin. Key technologies and understandings on the construction of smart fields [J]. Petroleum exploration and development, 2012, 39(1): 118-122.
- Yan Haijun, Jia Ailin, Guo Jianlin, et al. Gas-water controlling factors and distribution models of carbonate gas reservoir in the Longgang gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012, 32(1): 67-70.
- Jia Ailin, Yan Haijun, Guo Jianlin, et al. Development characteristics for different types of carbonate gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(5): 914-923.
- Guo Jianlin, Jia Ailin, He Dongbo, Tang Junwei, Ji Youliang. Sequence stratigraphy of upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous fan-delta outcrops in Luanping [J]. Geology in China, 2007,34(4):628-635.
- Yan Haijun, Guojianlin, Luochao, Jia Ailin, Ma Honghao, Wei Tiejun. Single sand body anatomy technology applied to gas flooding reservoir description [J]. Geoscience, 2015,29(6):1454-1466.
Yan Haijun
Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, China
Title: Optimization of enrichment area in low permeability water bearing gas reservoir

Biography:
Yan Haijun has received his BS degree in Petroleum Engineering from the Northeast Petroleum University and his MS degrees from Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development (RIPED), Beijing, China. From 2006, he has worked in the areas of oil & gas geology and gas development. He is currently the Engineer of Department of Ordos E&P, RIPED, working mainly on gas development. As an Engineer, he has published over 10 papers and 1 book
Abstract:
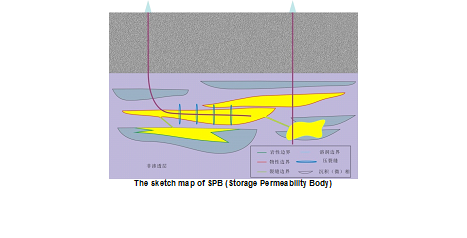
Low permeability gas reservoir is an important type of gas reservoir on a global scale. At present, a large number of low permeability water bearing gas reservoirs have been found in the world. In China, there are more than 2×104 m3 reserves distributed in this type reservoir. This kind of gas reservoir is mainly distributed in Sichuan and Ordos basin, China. This kind of gas reservoir is characterized by poor reservoir physical properties, strong heterogeneity, high water saturation, complex gas and water distribution and no obvious gas-water contact. So, the primary problem to develop this type reservoir is how to optimize the favorable area. Because of the complex formation water distribution, it is very hard to optimize the enrichment area to develop this kind of gas reservoir. Based on the two characteristics of storage and permeability and combing with the static and dynamic characteristics of the reservoir, it is an effective way to solve this problem that the reservoir is divided into different types. Gaoqiao gas reservoir is located in the Ordos basin and belongs to the low permeability water bearing gas reservoir. Take the Gaoqiao as an example, the classification criteria of storage permeability bodies are established and the type of drilled wells is classified. Based on the understanding of gas reservoir characteristics, the plane distribution of storage permeability body is drawn. Based on this distribution, we can optimize the development area in Gaoqiao. This method can be used to optimize the development area to develop such reserves. Furthermore, this method is helpful for the effective development of a large number of these gas reservoirs in China and the world.
Recent Publications:
- Jia Ailin, Yan Haijun. Problems and countermeasures for various types of typical carbonate gas reservoirs development[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2014, 35(3): 519-527.
- Yan Haijun, Jia Ailin, Guo Jianlin, et al. Gas-water controlling factors and distribution models of carbonate gas reservoir in the Longgang gas field, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2012, 32(1): 67-70.
- Jia Ailin, Yan Haijun, Guo Jianlin, et al. Development characteristics for different types of carbonate gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(5): 914-923.
- Yan Haijun, Jia Ailin, He Dongbo, Guo Jianlin, Yang Xuefeng, Zhu Zhanmei. Development problems and strategies of reef-shoal carbonate gas reservoir [J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014,25(3):414-422.
- Yan Haijun, Guojianlin, Luochao, Jia Ailin, Ma Honghao, Wei Tiejun. Single sand body anatomy technology applied to gas flooding reservoir description [J]. Geoscience, 2015,29(6):1454-1466.
Mohamad Gamil Abdalghani
University of Salahaddin, Iraq
Title: Evaluation study of different types adsorbents in minimizing sulfur contents in diesel fuel

Biography:
Mohamad Gamil Abdalghani has completed his PhD from Institute of Organic Chemistry with Petroleum Center, Bulgarian Academic for Science in Bulgaria, Sofia. He was the Director of Applied Chemistry Department in the University of Technology. He has then occupied the Directory of General Science Department in the College of Basic Education, University of Salahaddin and Directory of Laboratories and Imports at the same college. He has supervised many Msc and PhD students and he works as the Director of Scientific Promotion Committee.
Abstract:
Three types of adsorbents: Bentonite clay, silica gels, charcoal were selected to evaluate their behavior in minimizing sulfur contents in diesel fuel and to characterize the more efficient adsorbent. Native diesel fuel with sulfur contents of 0.8% was received in a temperature range between (250-320 oC) from fractional distillation of crude oil obtained from field of Kirkuk/Iraq with sulfur contents of 2% was used in this work. Desulfurization was performed in a continuous circulation of 150 ml of diesel fuel through a glass column (2 cm. i.d. × 25 cm length) containing 100 gm adsorbent by circulating pump. Adsorption for sulfur contents was investigated at different duration of times i.e., 2 hours, 4 hours and 6 hours. Bentonite exhibited the maximum desulphurization yield of 65% at 6 hours adsorption. Surface areas of all adsorbents were characterized by SEM and EDX analysis. The FT-IR study of the desulphurized diesel sample revealed that mostly high molecular weight thioles and thiophenic compounds were depleted during adsorption process.
Hassan Jalal Aziz
University of Salahaddin, Iraq
Title: The effect of some physical parameters on the performance of petroleum antioxidants additives

Biography:
Hassan Jalal Aziz is currently working as a Lecturer in University of Salahaddin, College of Basic Education, General Science Department. He has published many researches in the field of his specialization in international journals.
Abstract:
Three types of petroleum antioxidants additives; 2, 4-diteriarybutyl-1-phenol (Unol), tertiary alkyl primary amine with 9 carbon atoms (TAPA-9) and tertiary alkyl primary amine with 12 carbon atoms (TAPA-12) were selected to examine their anti-oxidation performance for crude diesel fuel. The study was included the effect of solubility and boiling point effect of these compounds on their efficiency as antioxidants during the oxidation process under elevated temperature. Chemiluminescence method was selected to detect the oxidation efficiency through the induction periods results. The solubility and the boiling points results was in the order of TAPA-12>TAPA-9>Unol. The resulted induction periods were 600, 440, 212 and 55 seconds for TAPA-12, TAPA-9, Unol and crude diesel respectively.
Xinyang Miao
China University of Petroleum, China
Title: Anisotropic optical response of oil shale at terahertz range
Time : 15:00-15:40

Biography:
Xinyang Miao is currently a PhD candidate in Material Science and Engineering at China University of Petroleum, Beijing, China. His main research interest is oil and gas optics, including rock physics and application of terahertz technology.
Abstract:
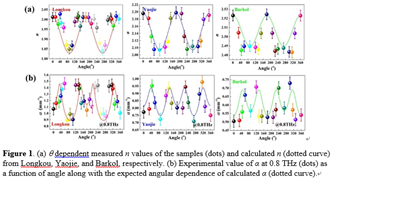
Oil shale, a finely grained sedimentary rock with kerogen contained, has been gradually developed in China since the 1920s. Numerous oil and gas products as fuels and raw materials in petrochemical industries can be yielded by pyrogenation of kerogen. Generally, shales as well as oil shales are often highly anisotropic owing to various combined effects. Ultrasonic measurements have demonstrated that the elastic properties are isotropic in the directions parallel to the bedding, while anisotropic in other directions. Owing to the unique advantages, Terahertz (THz) technique has been applied in various research areas of oil and gas exploration recently, including exploration and development of oil and gas reservoirs, transportation of oil-gas as well as evaluation of petrochemicals and pollutants. Meanwhile, THz technique has also been employed to study the anisotropic response of materials. In this paper, THz technique was employed to investigate anisotropic response of oil shales from Longkou, Yaojie and Barkol with different oil yield. All the samples had significant anisotropy of refractive index (n) and absorption coefficient (α) with symmetries at the location of 180°, which were corresponded with the bedding plane and the partial alignment of particles. Besides, the D-values of experiment n in the vertical and parallel direction of the bedding plane were calculated as Δn’=n^-n‖, and samples from Beipiao and Huadian were also tested in the horizontal and vertical directions for a sufficient number of THz parameters. Linear regression was built between the Δn’ of the samples from five regions and the oil yield, described as y=60.86x+3.72 for oil yield (y) and Δn’ (x), with the correlation coefficient R equaled 0.9866 and the residual sum of squares was 1.182, indicating THz technology could be an effective selection for evaluating the oil yield in oil shales from different regions.
Recent Publications:
- Xinyang Miao, et al. (2016) Oil yield characterization by anisotropy in optical parameters of the oil shale. Energy Fuels 30:10365−10370.
- Xinyang Miao, et al. (2017) Application of THz technology in oil and gas optics. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 60(2):024231
- Xinyang Miao, et al. (2017) Real-time monitoring the formation and decomposition processes of methane hydrate with THz spectroscopy. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 60(1):014221
- Xinyang Miao, et al. (2017) Discriminating the mineralogical composition in drill cuttings based on absorption spectra in the terahertz range. Applied Spectroscopy 71(2):186–193
- Rima Bao, Xinyang Miao, et al. (2016) Characterizing the oil and water distribution in low permeability core by reconstruction of terahertz images. Science China Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy 59(6):664201
Mohit Jhirwal
Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India
Title: Monitored laser grinding by real time nanobots data: A novel mud cake removal approach

Biography:
Mohit Jhirwal is a Graduate of Petroleum Engineering at Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University, India. He has been working for SPE PDPU Student Chapter for past 2 years and played instrumental role bagging Outstanding Chapter Award from SPE International.
Abstract:
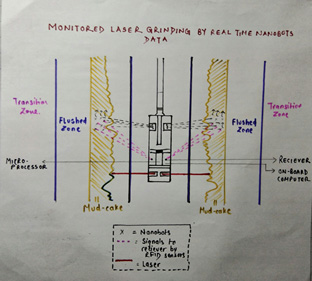
For ensuring casing and cementing quality, mud cake removal is essential. Various problems like stuck pipe take place because of the presence of mud cake. Mechanical methods of water jetting and chemical methods by means of acids, oxidizers, chelating agents and enzymes are currently employed for mud cake removal. However, water jetting can cause water blockage problems. Also, mud cakes of different permeability will be removed unevenly by same intensity water jets. Acids and oxidizers are very reactive but non-specific species, imposing several post perforation problems and formation damage. As an alternative, we propose a new method/device in this study with the usage of nanobots and laser grinding. The nanobots, placed in carrier, can be sent through drill string into the drill bit from where they can be deployed in all directions into the targeted zone. These non-adherent and self-propelled nanobots will move through the vertical permeability of the mud filtrate and would interpret the petro physical properties of the mud filtrate. The sensors would then send this data to molecular processor and with the help of radio frequency transmitter and receiver; we could immediately interpret the real time data from every point in the wellbore. This data would be used to change the intensity of the lasers in accordance with the petro physical properties. Lasers would then vaporize the mud cake according to its thickness and interpretation obtained and will grind the mud cake by creating popped holes. The precision and control over direction and power which laser provides could really be beneficial in mud cake removal and the same device could also be used for various other jobs like perforation and enhancing permeability during production phase. Nanotechnology integrated laser system holds great potential in removing mud cake efficiently and could significantly be useful in multilateral and horizontal wells.

Biography:
Mr. Mohammed Ali is an outstanding having brilliant analytical power which led to achieving his target. He proves his ability to be an independent thinker and motivated enough to carry out the assigned work on regularly basis. To begin with, he is an excellent student; with a lively curiosity that makes his dissatisfied with superficial explanations.
Abstract:
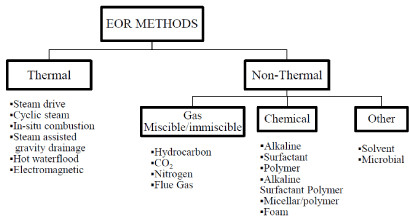
Statement of Enhance Oil Recovery is the way that nowadays using, due to the limit of coming years for the extraction of crude oil , and also due to the decreases of production of oil and gas from the reservoir. While the production of oil and gas for many years that production decreases due to the reserve estimation that had been calculated, also due to the decreases of reservoir pressure, so that the reduction of oil and gas production occurs. The major consideration is how to improve the production of oil and gas continuously as same the previous extraction quantities which were calculated by the study of reserve estimation of well. The main AIMS of EOR is to improve the extraction and production of oil and gas from the reservoir by the methods and techniques which is given by petroleum industry.
EOR methods and techniques:
1. EOR by Steam water well injection.
2. EOR by Natural gas well injection.
3. EOR by CO2 well injection.